Introduction to the Miyabi
Characteristics of the system
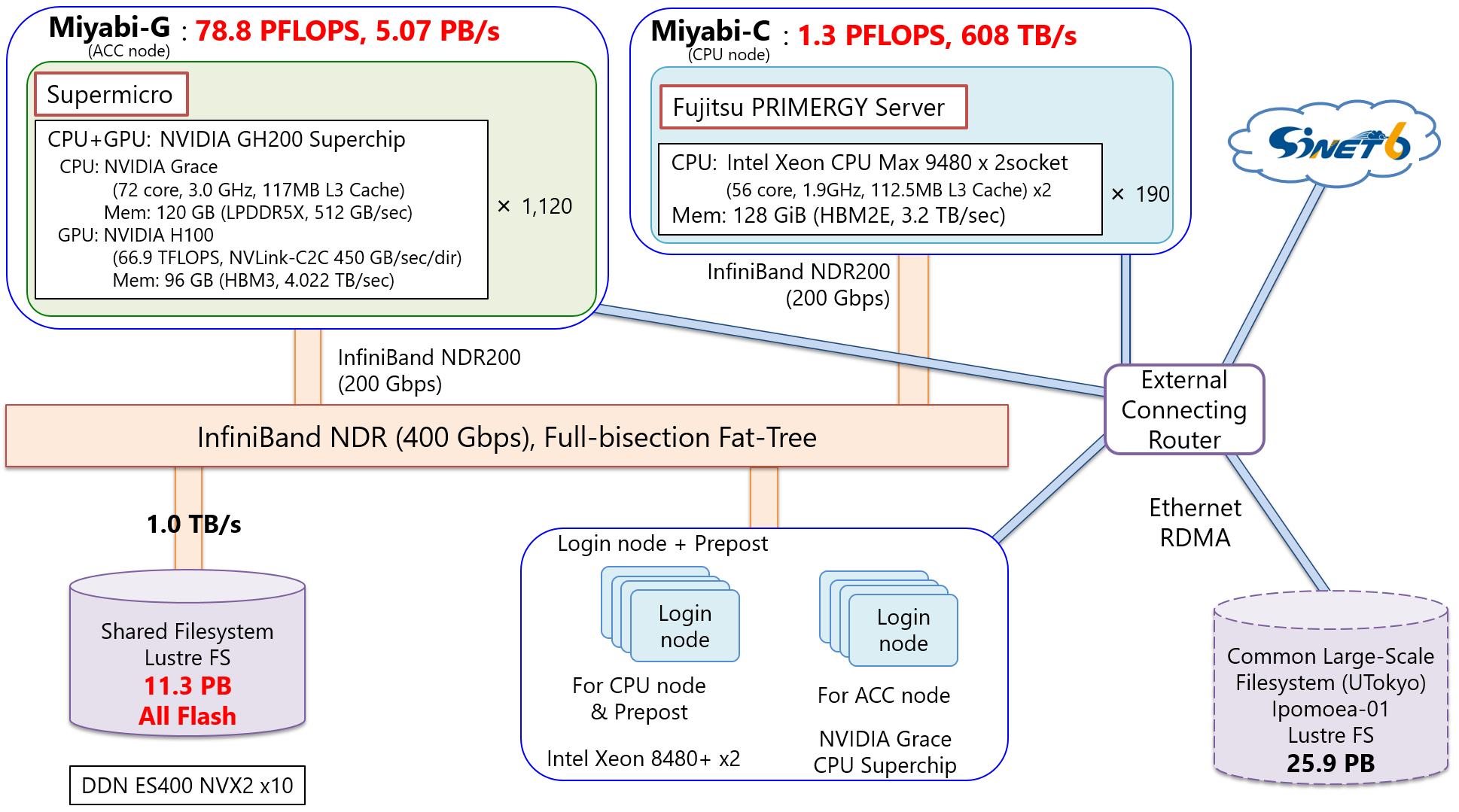
The Miyabi is a supercomputer system for shared use from the Joint Center for Advanced High Performance Computing (JCAHPC), operated jointly by the Information Technology Center, the University of Tokyo and the Center for Computational Sciences, University of Tsukuba. It is the largest massively parallel cluster supercomputer in Japan. The Miyabi, which has a double precision performance of 80.1 PFLOPS, consists of 1,120 compute nodes (Miyabi-G) equipped with NVIDIA's GH200 Grace-Hopper Superchip connected with NVLink-C2C, a dedicated ultra-fast CPU-GPU link, and 190 compute nodes equipped with two Intel's Xeon Max 9480 (Miyabi-C). It will be the first general-purpose large-scale system equipped with GH200 in Japan. It is also adopted with a 11.3 PB parallel file system that uses NVMe-SSD for all drives.
Hardware configuration
Overall configuration
| Item | Miyabi-G | Miyabi-C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total theoretical calculating performance | 78.8 PFLOPS | 1.29 PFLOPS | |
| Total number of nodes | 1,120 | 190 | |
| Total main storage capacity | 241.9 TB | 23.75 TiB | |
| Interconnect | InfiniBand NDR (200Gbps) | ||
| Network topology | Full-bisection Fat Tree | ||
| Shared file system | System name | Lustre(DDN EXAScaler) | |
| Server (OSS) | DDN ES400NVX2 | ||
| Number of servers (OSS) | 10 | ||
| Storage capacity | 11.3 PB | ||
| Storage data transmission speed | 1.0 TB/s | ||
Node configuration
| Item | Miyabi-G | Miyabi-C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine name | Supermicro ARS-111GL-DNHR-LCC | FUJITSU Server PRIMERGY CM2550 M7 | |
| CPU | Processor name | NVIDIA Grace CPU | Intel Xeon Max 9480 |
| Number of processors (number of cores) | 1 (72) | 2 (56+56) | |
| Frequency | 3.0 GHz | 1.9 GHz | |
| Theoretical calculating performance | 3.456 TFLOPS | 6.8096 TFLOPS | |
| Memory | 120 GB | 128 GiB | |
| Memory bandwidth | 512 GB/s | 3.2 TB/s | |
| GPU | Processor name | NVIDIA Hopper H100 GPU | - |
| Memory (unit) | 96 GB | ||
| Memory bandwidth (unit) | 4.02 TB/s | ||
| Theoretical calculating performance (unit) | 66.9 TFLOPS | ||
| Number of unit | 1 | ||
| CPU-GPU connection | NVLink C2C Cache-coherent (450 GB/s each direction per lane) |
||
Software configuration
| Item | Miyabi-G | Miyabi-C |
|---|---|---|
| OS | Rocky Linux 9 (login node is Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9) | |
| Compiler | GNU Compiler | |
| NVIDIA HPC SDK (Fortran, C, C++, OpenMP, OpenACC) NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit (CUDA C, CUDA C++) |
Intel Compiler (Fortran, C, C++) | |
| Message passing library | Open MPI, NVIDIA HPC-X | Intel MPI |
| Library | cuBLAS, cuSPARSE, cuFFT, MAGMA, cuDNN, NCCL | - |
| BLAS, CBLAS, LAPACK, ScaLAPACK, SuperLU, SuperLU MT, SuperLU DIST, METIS, MT-METIS, ParMETIS, Scotch, PT-Scotch, PETSc, Trillinos, FFTW, GNU Scientific Library, NetCDF, Parallel netCDF, HDF5, Parallel HDF5, OpenCV, Xabclib, ppOpen-HPC, MassiveThreads, Standard Template Library (STL), Boost C++ | ||
| Applications | OpenFOAM, ABINIT-MP, PHASE, FrontFlow/blue, FrontISTR, REVOCAP-Coupler, REVOCAP-Refiner, OpenMX, MODYLAS, GROMACS, BLAST, R packages, bioconductor, BioPerl, BioRuby, BWA, GATK, SAMtools, Quantum ESPRESSO, Xcrypt, ROOT, Geant4, LAMMPS, CP2K, NWChem, DeepVariant, Paraview, Vislt, POV-Ray, TensorFlow, PyTorch, JAX, Keras, Horovod, MXNet, Miniforge, Kokkos | |
| - | MATLAB | |
| Free software | autoconf, automake, bash, bzip2, cvs, emacs, findutils, gawk, gdb, make, grep, gnuplot, gzip, less, m4, python, perl, ruby, screen, sed, subversion, tar, tcsh, tcl, vim, zsh, git, Julia, CMake, Ninja, Java JDK, Grid Community Toolkit, Gfarm, FUSE, etc. | |
| Container virtualization | Apptainer, Singularity Community Edition | |