Introduction to the Reedbush Supercomputer System
Characteristics of the system
Reedbush is composed of three subsystems: Reedbush-U, which comprises only CPU nodes; Reedbush-H, which comprises nodes with two GPU mounted as computational accelerators; and Reedbush-L, which comprises nodes with four GPU mounted. These subsystems can be operated as independent systems. This is the first time that the Information Technology Center, the University of Tokyo has adopted a computational accelerator in a supercomputer system, and its aim is to meet the needs of new fields, including big data analysis and machine learning.
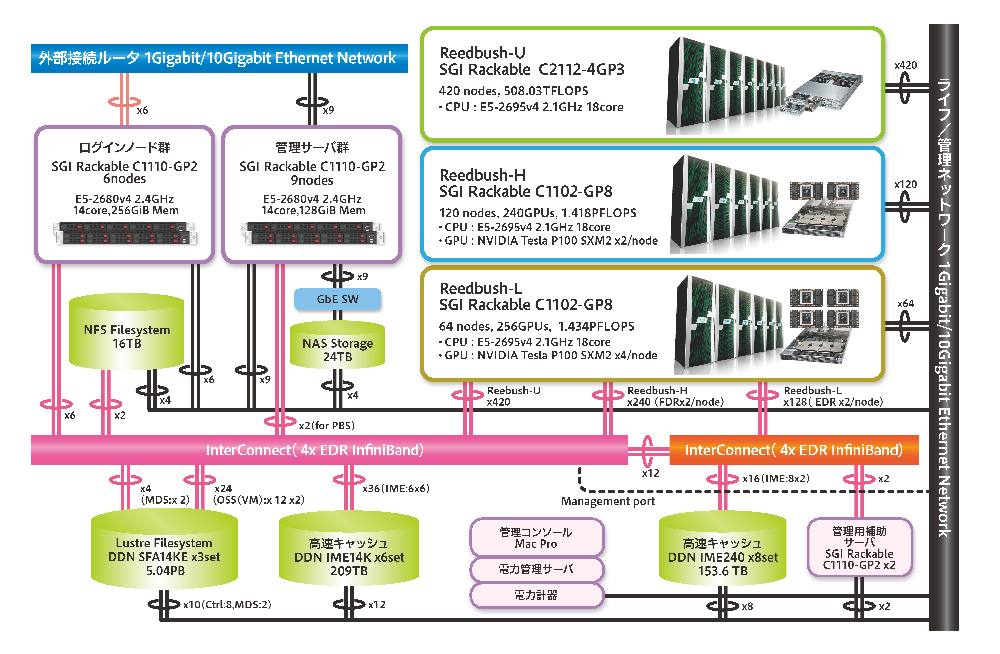
Hardware configuration
Overall configuration
| Item | Reedbush-U | Reedbush-H | Reedbush-L | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall system (Computation nodes) |
Total theoretical computational performance | 508.03 TFlops | 1418.2 TFlops | 1435.3 TFlops | |
| Total number of nodes | 420 | 120 | 64 | ||
| Total memory | 105 TByte | 30 TByte | 16 TByte | ||
| Network topology | Full-bisection Fat Tree | ||||
| Parallel file system | System name | Lustre file system | |||
| Server (OSS) | DDN SFA14KE | ||||
| Number of servers (OSS) | 3 | ||||
| Storage capacity | 5.04 PB | ||||
| Transmission speed | 145.2 GB/sec | ||||
| Fast file cache systems | Server | DDN IME14K | DDN IME240 | ||
| Number of servers | 6 | 8 | |||
| Capacity | 209 TB | 153.6 TB | |||
| Transmission speed | 436.2 GB/sec | 166.4 GB/sec | |||
Node configuration
| Item | Reedbush-U | Reedbush-H | Reedbush-L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machine name | SGI Rackable C2112-4GP3 |
SGI Rackable C1102-GP8 |
SGI Rackable C1102-GP8 |
|
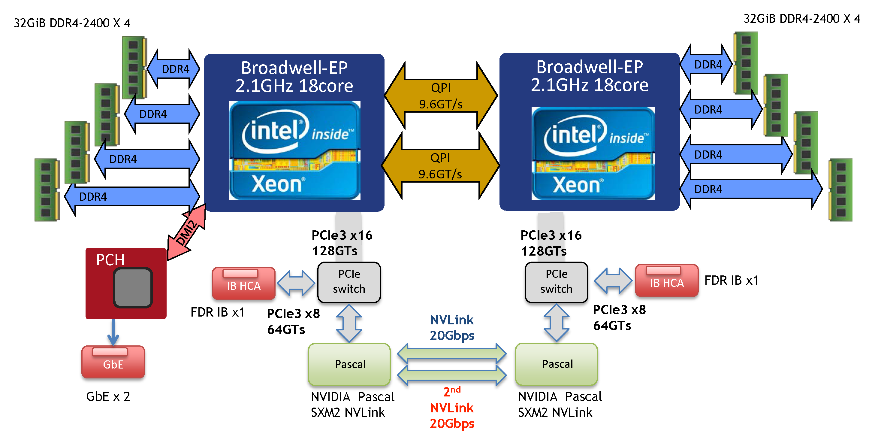
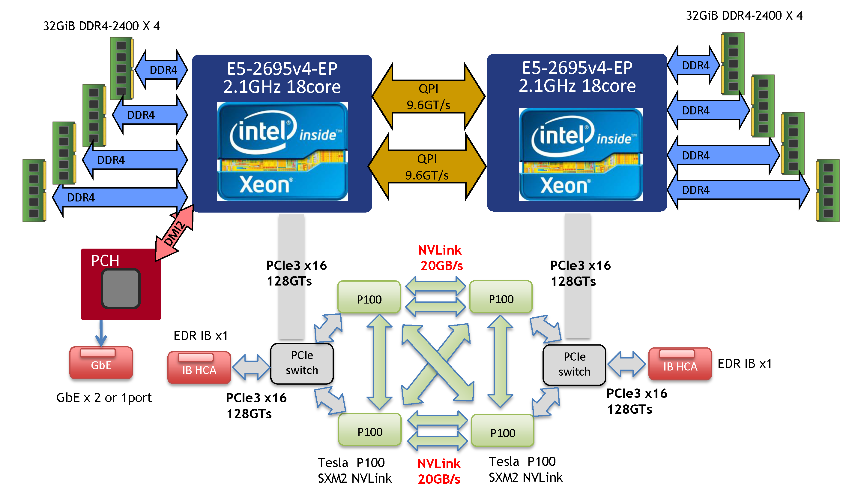
| CPU | Processor name | Intel Xeon E5-2695v4 (Broadwell-EP) | ||
| Number of processors (number of cores) | 2 (36) | |||
| Frequency | 2.1 GHz (Maximum 3.3 GHz when TBT) | |||
| Theoretical calculating performance | 1209.6 GFlops | |||
| Memory Capacity | 256 GB | |||
| Memory bandwidth | 153.6 GB/sec | |||
| GPU | Processor name | None | NVIDIA Tesla P100 (Pascal) | |
| Number of cores (standalone) | 56 | |||
| Storage capacity (standalone) | 16 GB | |||
| Memory bandwidth (standalone) | 732 GB/sec | |||
| Theoretical computational performance (standalone) | 5.3 TFlops | |||
| Number mounted | 2 | 4 | ||
| Connection between CPU-GPU/td> | PCI Express Gen3 x16 lanes (16 GB/sec) |
|||
| Connection between GPU | NVLink 2 brick (20 GB/sec x2) |
NVLink 2 brick (20 GB/sec x1 or 2) |
||
| Interconnections | InfiniBand EDR 4x (100 Gbps) |
InfiniBand FDR 4 x 2 links (56 Gbps x2) |
InfiniBand EDR 4 x 2 links (100 Gbps x2) |
|
Software configuration
| Item | Reedbush-U | Reedbush-H/L |
|---|---|---|
| OS | Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 | |
| Compiler | GNU Compiler Intel Compiler (Fortran77/90/95/2003/2008, C, C++) |
|
| None | PGI compiler (Fortran77/90/95/2003/2008, C, C++, OpenACC 2.0, CUDA Fortran) NVCC compiler (CUDA C) |
|
| Message communication library | Intel MPI, SGI MPT, Open MPI, MVAPICH2, Mellanox HPC-X | |
| None | GPUDirect for RDMA: OpenMPI, MVAPICH2-GDR | |
| Library | Intel’s Math Kernel Library (MKL), BLAS, LAPACK, ScaLAPACK, Other Libraries, FFTW, GNU Scientific Library, NetCDF, Parallel netCDF, Xabclib, ppOpen-HPC, ppOpen-AT, MassiveThreads, and OpenJDK | |
| SuperLU, SuperLU MT, SuperLU DIST, METIS, MT-METIS, ParMETIS, Scotch, PT-Scotch, PETSc and Boost | cuBLAS, cuSPARSE, cuFFT, MAGMA, OpenCV, ITK, Theano, Anaconda, ROOT and TensorFlow | |
| Applications | OpenFOAM, ABINIT-MP, PHASE, FrontFlow/blue, FrontISTR, REVOCAP, OpenMX, xTAPP, AkaiKKR, MODYLAS, ALPS, feram, GROMACS, BLAST, R, Bioconductor, BioPerl, BioRuby, BWA, GATK, SAMtools, K MapReduce and Spark | Torch, Caffe, Chainer, GEANT4 |
| Debugger, profiler | Total View, Intel VTune, Intel Trace Analyzer & Collector, PerfSuite, NVIDIA Visual Profiler | |
| Free software | Autoconf, automake, bash, bzip2, cvs, emacs, findutils, gawk, gdb, make, grep, gnuplot, gzip, less, m4, python,perl, ruby, screen, sed, subversion, tar, tcsh, tcl, vim, zsh, cmake, HDF5, git, etc. | |
